Luminescent AIE Dots for Anticancer Photodynamic Therapy
Release time:2023-07-15
Hits:
Journal:Front. Chem
Volume:9
Key Words:photodynamic therapy, photosensitizers, aggregation-induced emission, AIE dots, theranostics
DOI number:10.3389/fchem.2021.672917
Date of Publication:2021-05-25
Impact Factor:5.221
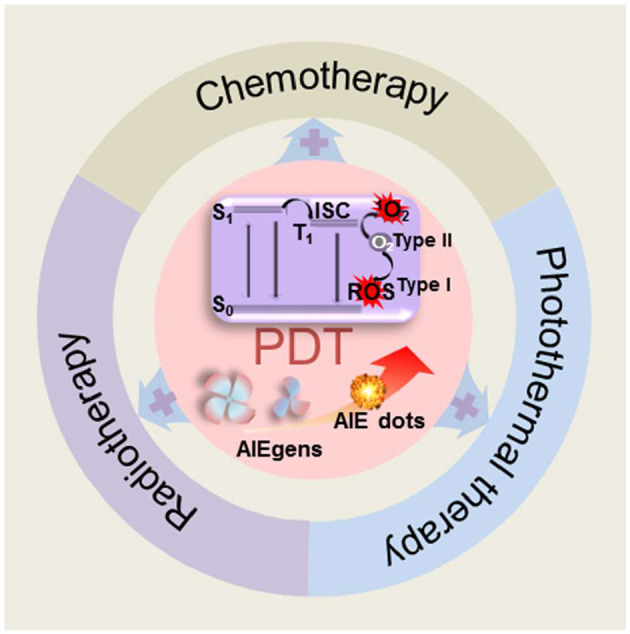
Abstract:Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an emerging effective strategy for cancer treatment. Compared with conventional cancer therapies, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, PDT has shown great promise as a next-generation cancer therapeutic strategy owing to its many advantages such as non-invasiveness, negligible observed drug resistance, localized treatment, and fewer side effects. One of the key elements in photodynamic therapy is the photosensitizer (PS) which converts photons into active cytotoxic species, namely, reactive oxygen species (ROS). An ideal PS for photodynamic therapy requires the efficient generation of ROS, high stability against photo bleaching, and robust performance in different environments and concentrations. PSs with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics have drawn significant attention, in that they can overcome the aggregation- caused quenching effect that is commonly seen in the case of fluorescence dyes and provide excellent performance at high concentrations or in their condensed state. Moreover, organic nanomaterials with AIE characteristics, or AIE dots, have played an increasingly significant role in assisting PDT based on its excellent ROS generation efficiency and simultaneous imaging feature. This review summarizes the recent advances on the molecular design of AIE PSs and AIE dots-based probes, as well as their emerging applications for enhanced anticancer PDT theranostics.