Boosting the Photodynamic Degradation of Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Aggregates Via a “Bait-Hook-Devastate” Strategy
Release time:2021-09-24
Hits:
Journal:ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
Volume:13
Issue:13
Page Number:14911-14919
ISSN No.:1944-8244
Key Words:amyloidogenic diseases
amyloid aggregates
photodynamic degradation
polymer
electrostatic interaction
DOI number:10.1021/acsami.1c00082
Date of Publication:2021-03-25
Impact Factor:8.758
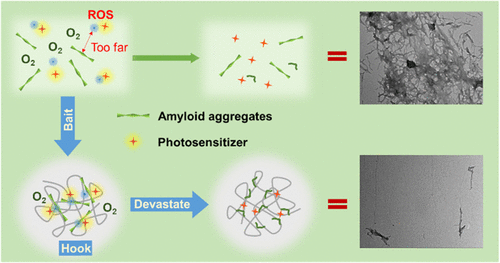
Abstract:Photosensitizers that can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon irradiation have emerged as promising agents for photodynamic degradation of toxic amyloid aggregates that are linked to many amyloidogenic diseases. However, due to the ultrastable β-sheet structure in amyloid aggregates and inefficient utilization of the generated ROS, it usually requires high stoichiometric concentration of the photosensitizer and/or intensive light irradiation to fully dissociate aggregates. In this work, we have developed a “bait-hook-devastate” strategy to boost the efficiency of the photodynamic degradation of amyloid aggregates. This strategy employs anionic polyacrylic acid as a bait to accumulate cationic human islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) aggregates and positively charged photosensitizer TPCI in a confined area through electronic interactions. Multiple characterization studies proved that the utilization rate of ROS generated by TPCI was remarkably improved via this strategy, which amplified the ability of TPCI to dissociate IAPP aggregates. Rapid and complete degradation of IAPP aggregates could be achieved by irradiating the system under very mild conditions for less than 30 min, and the IAPP-mediated cytotoxicity was also largely alleviated, providing a new paradigm to accelerate photodynamic degradation of amyloid aggregates for further practical applications.
Links to published journals:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.1c00082