个人信息
Personal information
教授 博士生导师 硕士生导师
性别:男
在职信息:在职
所在单位:材料科学与工程学院
学历:研究生(博士)毕业
学位:工学博士学位
毕业院校:华中科技大学
学科:材料加工工程曾获荣誉:
2017 华中科技大学学术前沿青年团队负责人
2017 黄鹤英才“专项”计划
2016 江苏省双创人才
2016 华中科技大学师德三育人奖
论文类型:期刊论文
发表刊物:Acta Biomaterialia
收录刊物:SCI
学科门类:工学
一级学科:材料科学与工程
文献类型:J
卷号:153
页面范围:614-629
关键字:Additive manufacturing;Laser powder bed fusion;Corrosion fatigue;Zinc-magnesium;Triply periodic minimal surface
DOI码:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.09.047
发表时间:2022-09-23
影响因子:10.633
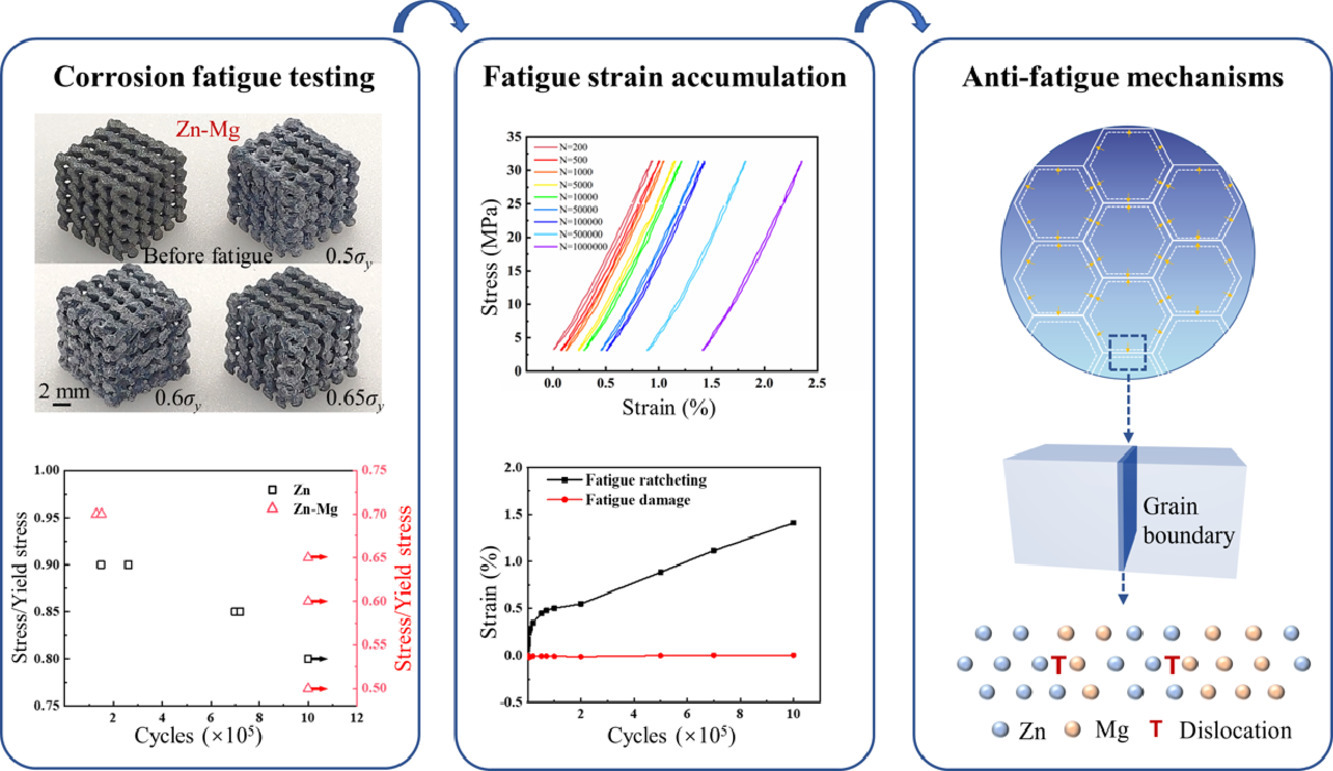
摘要:Additively manufactured biodegradable zinc (Zn) alloy scaffolds constitute an important branch in orthopedic implants because of their moderate degradation behavior and bone-mimicking mechanical properties. This work investigated the corrosion fatigue response of a zinc-magnesium (Zn-Mg) alloy gyroid scaffold fabricated via laser-powder-bed-fusion additive manufacturing at the first time. The high-cycle compression-compression fatigue testing of the printed Zn-Mg scaffold was conducted in simulated body fluid, showing its favorable fatigue strength, structural reliability, and anti-fatigue capability. The printed Zn-Mg scaffold obtained a 227% higher fatigue strength than that of the printed Zn scaffold but 17% lower strain accumulation at 106 cycles. The accumulative strain of the Zn-Mg scaffold at its fatigue strength was dominant by fatigue ratcheting, since the fatigue damage strain of the scaffold was approximately zero. The corrosion products (ZnO and Zn(OH)2) were conducive to the inhibition of fatigue ratcheting and fatigue damage. Dislocation pile-up and solid solution phases at the grain boundaries of the Zn-Mg scaffold could retard the spreading of the crack tip and impede excessive grain coarsening, improving its fatigue endurance limit. Notably, the printed Zn-Mg scaffold could dissipate the fatigue energy through moderate grain boundary migration, thus reducing its plastic deformation. These findings illuminated the anti-fatigue mechanisms related to microstructural features and corrosive environments and highlighted the promising prospects of additively manufactured Zn-Mg scaffolds in orthopedic applications.
发布期刊链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2022.09.047
