Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
Supervisor of Master's Candidates
Gender:Male
Status:Employed
Department:School of Life Science and Technology
Education Level:Postgraduate (Doctoral)
Discipline:Biomedical Engineering
Paper Publications
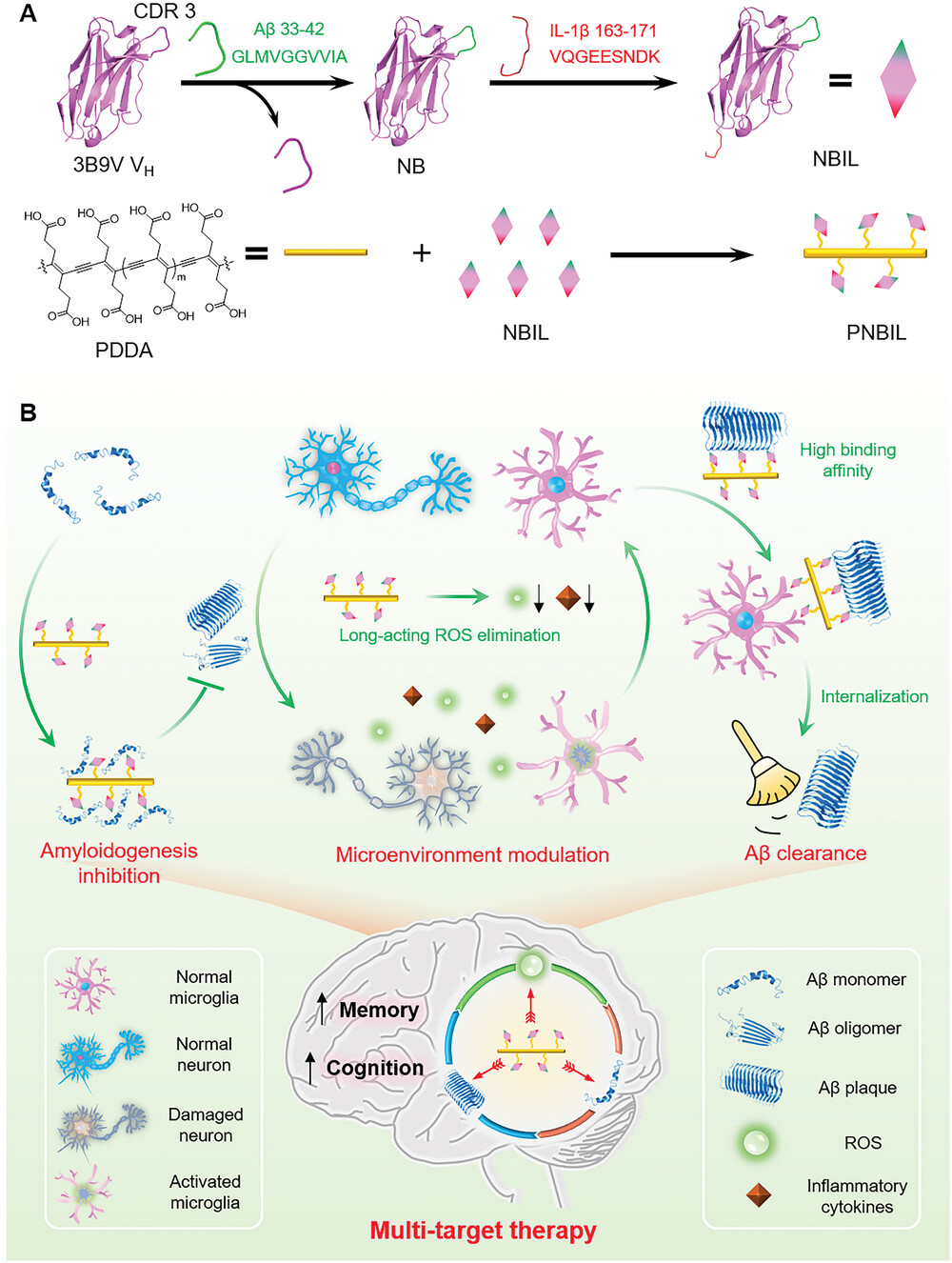
Multivalent Nanobody Conjugate with Rigid, Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Scaffold for Multi-Target Therapy of Alzheimer's Disease
Indexed by:Journal paper
Journal:Advanced Materials
Included Journals:SCI
Discipline:Engineering
First-Level Discipline:Biomedical Engineering
Document Type:J
Volume:35
Issue:17
Page Number:2210879
DOI number:10.1002/adma.202210879
Date of Publication:2023-02-14
Impact Factor:32.086
Abstract:Efficient therapeutic strategies that concurrently target both Aβ aggregation and oxidative stress in the Alzheimer's disease (AD) microenvironment emerge as a cutting-edge tool to combat the intricate pathogenesis of AD. Here, a multivalent nanobody conjugate with rigid, reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging scaffold is developed to achieve simultaneous Aβ amyloidogenesis mitigation, ROS elimination, and Aβ plaque clearance. Grafting Aβ segment (33-GLMVGGVVIA-42) into the third complementary-determining region of a parent nanobody generates an engineered nanobody NB that can recognize Aβ and inhibit its aggregation through homotypic interactions. NB is further genetically modified with a fragment of human interleukin-1β (163-VQGEESNDK-171), so that the obtained fusion nanobody NBIL can also facilitate the Aβ clearance by microglia. Linking NBIL covalently onto a rigid, ROS scavenging scaffold poly(deca-4,6-diynedioic acid) (PDDA) creates the multivalent nanobody conjugate PNBIL, which not only boosts the binding affinity between NBIL and Aβ aggregates for nearly 100 times but also possesses a long-term capability of oxidative stress alleviation, inflammation reduction, and neuron protection. PNBIL has significantly attenuated symptoms on two AD mouse models through amyloidogenesis inhibition and AD microenvironment modulation, validating that the multivalent nanobody conjugate design based on combinatory nanobody and molecular engineering is a promising approach of multi-target therapeutic strategies.
Links to published journals:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202210879
