个人信息
Personal information
副教授 博士生导师 硕士生导师
性别:男
在职信息:在职
所在单位:光学与电子信息学院
学历:研究生(博士)毕业
学位:工学博士学位
毕业院校:英国南安普敦大学 the University of Southampton, UK
学科:光学工程光学
曾获荣誉:
2024 湖北省第五批“科技副总”
2021 国际电气与电子工程师协会高级会员(IEEE senior member)
2020 华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院突出贡献奖
2019 欧盟玛丽居里学者人才计划Marie-Curie Fellowship
2019 华中科技大学教师教学竞赛奖二等奖
2019 湖北省优秀学士学位论文指导教师
2015 华中科技大学大学生科技创新活动优秀指导教师
论文类型:期刊论文
论文编号:106906
第一作者:邓柏涛
通讯作者:司马朝坦
合写作者:鲁平,刘德明
发表刊物:Optics and Lasers in Engineering
收录刊物:SCI、EI
所属单位:Elsevier
学科门类:工学
一级学科:光学工程
文献类型:J
卷号:151
ISSN号:0143-8166
关键字:Feedback monitoring; Half-wave scanning; Low sampling rate; Nonlinear scanning; TDLAS
DOI码:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2021.106906
发表时间:2021-12-13
影响因子:4.836
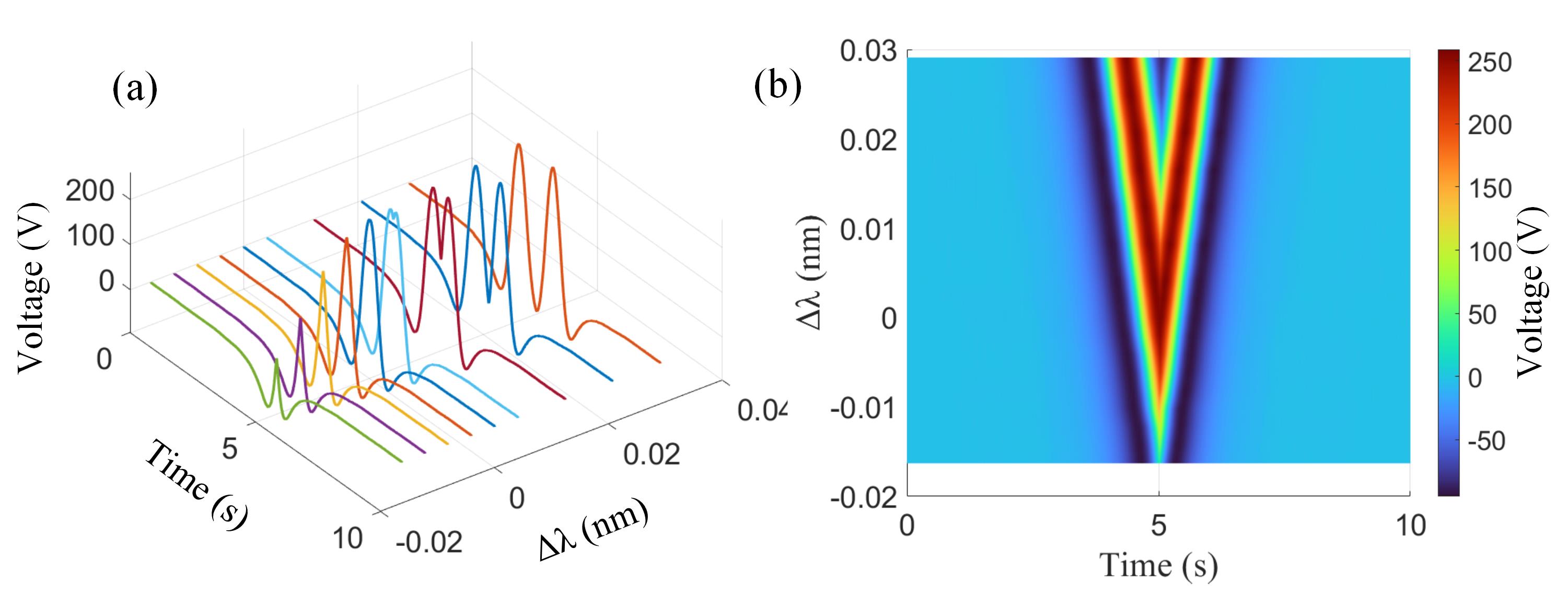
摘要:Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) for trace gas sensing has been investigated widely. Conventional wavelength-modulation spectroscopy (WMS) in TDLAS usually involves linear triangle patterns for tunable laser scanning. Here, a novel modified laser scanning technique is proposed and experimentally demonstrated in the WMS-based TDLAS gas sensor. The half-wave scan is primarily introduced to drive the laser diode to cover 1/2 range of the Lorentz-like gas absorption line. By monitoring waveform derivation of second harmonics, real-time status of the laser output could be exhibited and the output wavelength constancy can be controlled. It is also verified that second harmonics feature basically linearly with wavelength drifts, allowing the in-situ regulation of laser wavelength stability. Moreover, the nonlinear half-wave scan is introduced and designs a nonlinear function across the scanning pattern. It enlarges the temporal window around strong absorption and consequently acquires additional valuable waveform data. With the limited sampling rate for TDLAS signal processing, by using the nonlinear half-wave scan, second harmonics fluctuate merely 1/3 of that in the conventional WMS-2f linear scan. The proposed modified laser scanning technique is employed in a methane sensor, realizing about 3 ppm minimum detection limit and 9.6 ppm measurement accuracy. This technique is beneficial and universal for real-time monitoring and in-situ control of laser sources and improvement in accuracy and stability for current WMS-based TDLAS gas detection.
-
上一条:
Ultra-sensitive ppb-level methane detection based on NIR all-optical photoacoustic spectroscopy by using differential fiber-optic microphones with gold-chromium composite nanomembrane
-
下一条:
Design and Analysis of Ultra-Wideband Highly-Birefringent Bragg Layered Photonic Bandgap Fiber With Concave-Index Cladding
